Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
Using sensor data for numerical models
Published:
Sensor data have become an important tool in oceanographic science in recent years. Their low cost and relative ease of production have made them an invaluable tool in getting more information about the complex dynamical systems that govern the ocean. Recent additions include, but are not limited to microSWIFT , OpenMetBuoy (OMB) and MELODI. And while these sensors are great, the cost still lies at about 1000 USD due to the need for robust communication using technologies like Iridium and GSM. We aim to create a cheap and open source buoy to measure how the water flows in coastal environments such as a fjord. In these environments, we hope to be able to transmit the data using Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) technology, which is both cheaper and less power hungry than the aforementioned GSM and Iridium technologies.
portfolio
Succesful radio test at Sognsvann
Image showing each radio message sent during a walk around Sognsvann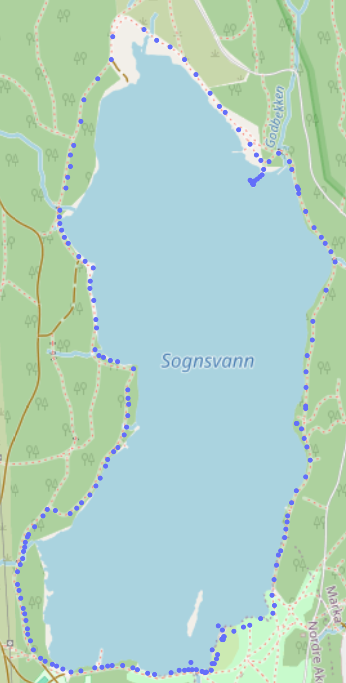
publications
Modeling CSF circulation and the glymphatic system during infusion using subject specific intracranial pressures and brain geometries
Published in Fluids and Barriers of the CNS, 2024
In this paper, we model the procedure of infusion tests on the human brain. Infusion tests are used to check if patients diagnosed with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) are likely to benefit from surgery. To model these, we implemented a numerical model based on flow in porous media on 47 different geometries constructed from MRI scans of the human brain and with data from infusion tests performed on the same subjects.
Recommended citation: Dreyer et al. (2024). "Modeling CSF circulation and the glymphatic system during infusion using subject specificintracranial pressures and brain geometries." Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. 21,82.
Download Paper
Direct in-situ observations of wave-induced floe collisions in the deeper Marginal Ice Zone
Published in Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2025
In this article, we present raw acceleration data recovered from a buoy placed on an ice sheet in the arctic marginal ice zone in 2020. We found anomalous and extreme acceleration events in some parts of the recovered data. These events are both phase locked with the wave field and unidirectional, making collisions between ice floes a likely candidate for these events.
Recommended citation: Dreyer et al. (2025). "Direct in-situ observations of wave-induced floe collisions in the deeper Marginal Ice Zone" Cold Regions Science and Technology2025.104642
Download Paper
OLB: An Open Lora Buoy for Coastal Water Measurements
Published in Arxiv, 2025
In this article, we present a new design for a oceanographic drifter created to measure ocean currents in coastal environments. The drifter offers months of battery time, at a cost of about 100 € each and comes with included functionality to make recovery easier.
Recommended citation: Dreyer et al. (2025). "OLB: An Open Lora Buoy for Coastal Water Measurements" An arxiv preprint,
Download Paper
teaching
MEK4600 - Experimental Fluid Mechanics
Graduate course, University of Oslo, Department of Mathematics, 2022
I thought a lab module in experimental fluid mechanics about the construction and development of sensor buoys using Long Range radio technology.
MEK2200 - Continuum mechanics
Workshop, University of Oslo, Department of Mathematics, 2024
Some lectures on solid mechanics, and exercise sessions. I also developed several exercise sets. Had the course for the fall semesters 2024 and 2025. Link to course web page: https://www.uio.no/studier/emner/matnat/math/MEK2200/
